The most innovative and sustainable office building in the world

It is called ‘The Edge’ and is located in the business district of Amsterdam, in the Netherlands
It is called ‘The Edge’ and is located in the business district of Amsterdam, in the Netherlands
The Edge -a 40,000m² office building- may be the world's most sustainable and 'smartest' one, able to constantly monitor its energy consumption and adapt through new technologies and innovation. It was designed for the global financial firm and main tenant, Deloitte, by London-based architects PLP Architecture and the project was developed by Dutch firm OVG.
In December 2014, the Edge received the highest ever BREEAM score (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Methodology) which has become the de facto test for sustainability in buildings: an outstanding 98.36% rating. The building was also awarded the BREEAM Award for Offices New Construction in 2016, and won the public vote for the prestigious Your BREEAM Award.
Here are some of the building’s innovations
· ‘Smart’ ceilings, embedded with 28,000 sensors, continuously measure temperature, light, motion and humidity, allowing the building to automatically adjust energy use.
· There is ‘smart’ lighting - each one of the LED panels is ultra-efficient and requires only a tiny amount of electricity.
· Employees are able to control the temperature, lighting and blinds via a series of apps on their smart phones, as well as to book meeting rooms, open lockers and check in to their desks.
· The roof and the south-facing facade incorporate the largest array of photovoltaic panels of any European office building.
· The rain water collected on the roof is used to flush toilets and irrigate the green terraces in the atrium and other garden areas surrounding the building.
· An aquifer thermal energy storage system (with two 129m deep wells) allows thermal energy differentials to be stored deep underground, providing all of the energy required for heating and cooling. A heat-pump was also applied to this storage system to increase efficiency.
· The greenspace that separates the building from the nearby motorway acts as an ecological corridor, allowing animals and insects cross the site safely.
An informative video on the Edge follows:
Media
Want to read more like this story?

UK’s first energy-positive office opens in Swansea
Jul, 16, 2018 | NewsThe UK's first energy-positive classroom generates more than one and a half times the solar energy i...

EU Parliament is updating the EU's rules to further improve the energy efficiency of buildings
Apr, 12, 2018 | NewsFrom January 1st, 2021, all new buildings in the EU should use little or no energy for heating, cool...
The prospects for carbon-neutral buildings
Oct, 27, 2023 | NewsIn the United Kingdom, buildings account for 33% of greenhouse gas emissions and 40% of global ener...

The "living building" in Georgia Tech University
Apr, 22, 2021 | NewsGeorgia Tech announced on Earth Day 2021 that one large project, the Kendeda building has been...

World Sustainable Energy Days 2018 in Wels, Austria
Feb, 01, 2018 | NewsOne of the largest conferences on sustainable energy One of the largest conferences on sustainable...

The Internet of Things in building industry
Aug, 01, 2021 | NewsThe Internet of Things (IoT) is currently developed and can be applied to the building industry gene...

Building collapse south of Indianapolis: 2 workers injured
Apr, 04, 2022 | NewsA building under construction collapsed, injuring at least two construction workers, authorities sa...
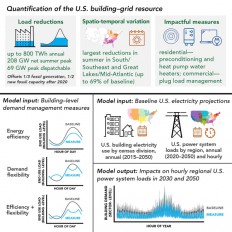
Control building energy demand to preserve the electrical power resources
Jul, 07, 2021 | NewsA new study conducted in the United States quantifies how the optimization of the consumed energy in...

3-story building collapses in Brooklyn, New York
Jul, 07, 2020 | NewsA 3-story building that used to house a gym facility suddenly gave way in Brooklyn. The incident...
Trending

Vertical gardens in Mexico City to combat pollution

Saudi Park Closed After 360 Big Pendulum Ride Crashes to Ground, 23 injured

Characteristics of Load Bearing Masonry Construction

Taipei 101’s impressive tuned mass damper

Dutch greenhouses have revolutionized modern farming

Federal court rules Biden’s offshore drilling ban unlawful


